
of
Europe's surface has major problems with drought, according to the European Commission.
In 17 percent of the continent, the situation is acute.
- It is very scary, says Niclas Hjerdt, hydrologist at SMHI. The low water levels in the Rhine River are causing problems with cargo ships that are getting harder and harder to pass.
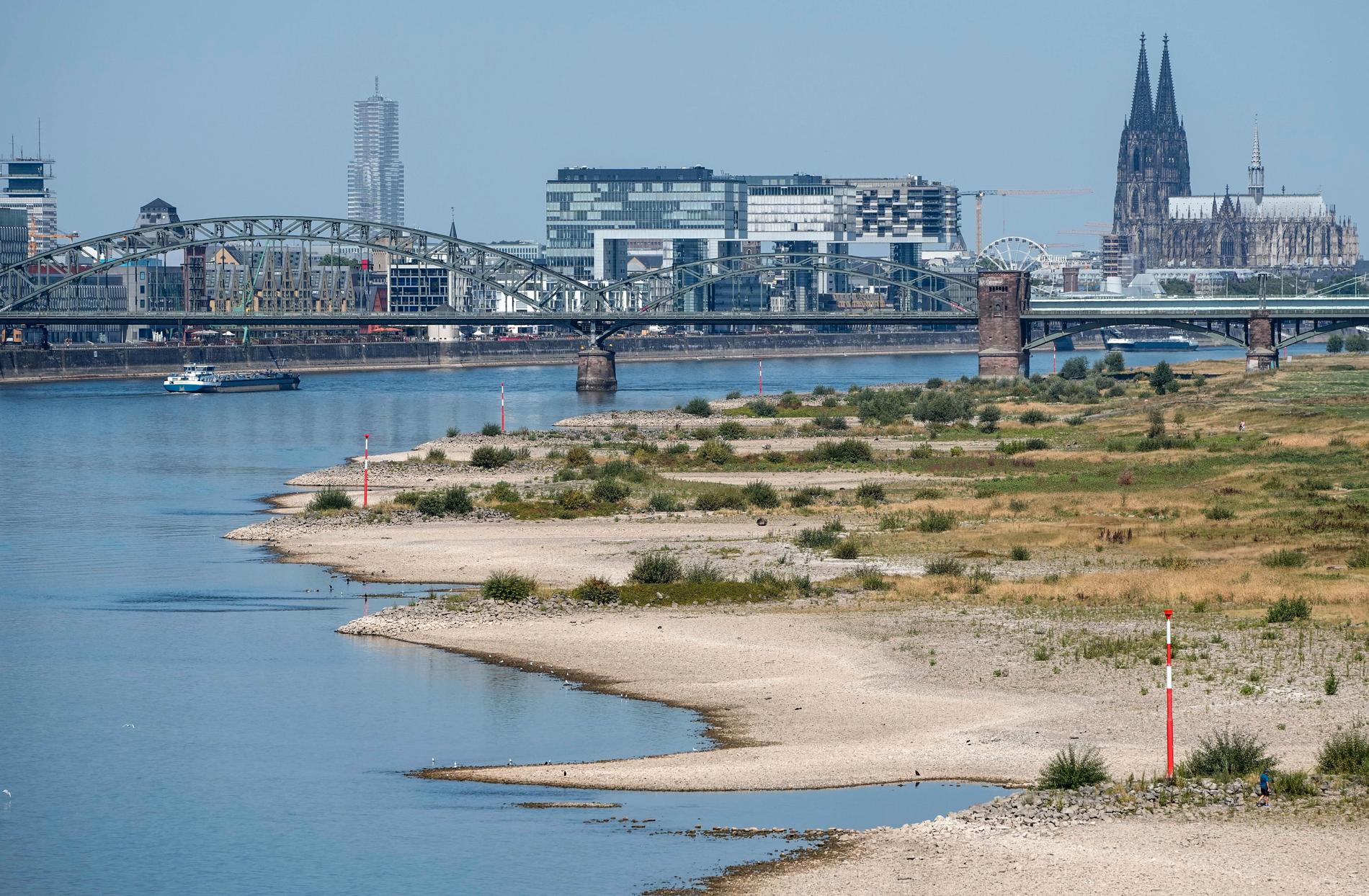

The low water levels in the Rhine River are causing problems with cargo ships that are getting harder and harder to pass. Photo: Martin Meissner / AP
Almost half of Europe's surface, 47 percent, is affected by drought. This is shown by the European Commission's drought observatory on a new map of the situation in the continent. At the same time, the situation is acute on 17 percent of the surface.
Some of the places hardest hit are the UK, Spain, France and Germany. Even in parts of northern Sweden, the situation is assessed as urgent, according to the map.
- It is very serious from two aspects. One is the record low levels in the waterways. The second is that it is a recurring event that is happening more and more frequently in Europe, says Johan Rockström, head of the German Potsdam Institute for Climate Research.
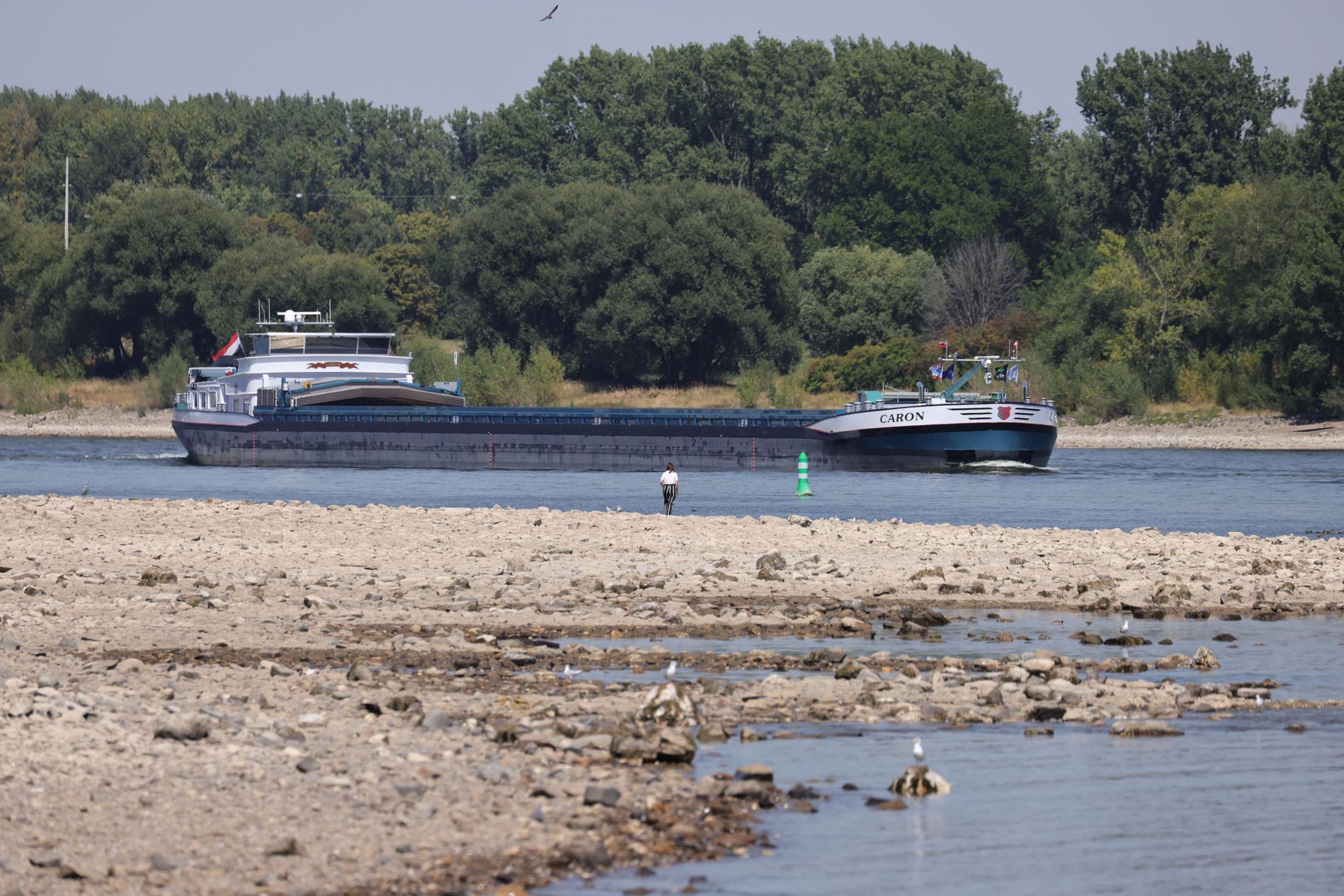

Cargo ships traveling across the Rhine, where the water level is getting lower and lower, cannot fill the entire cargo. Photo: GETTY IMAGES .
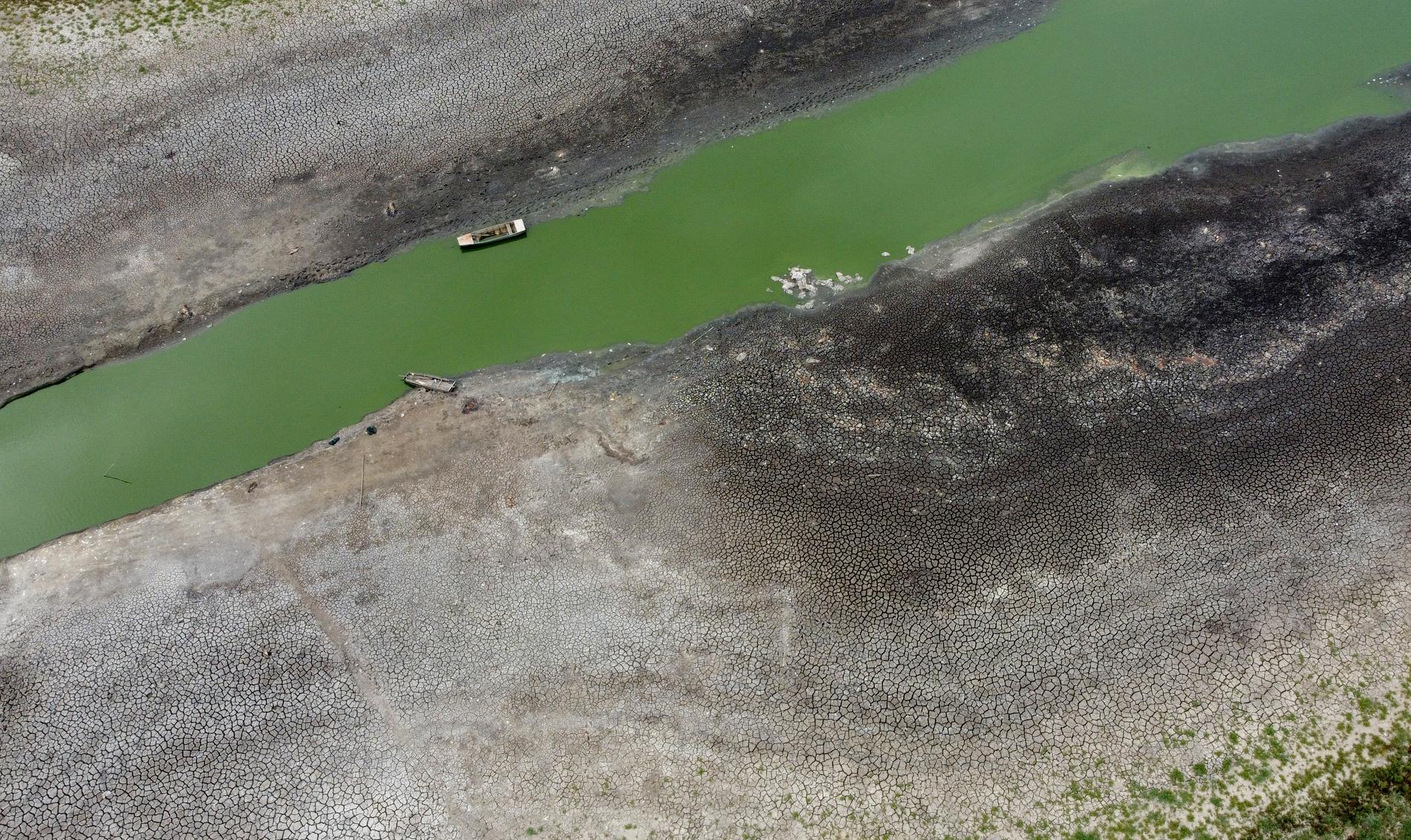

A dried up lake northwest of Belgrade. Serbia is one of the European countries affected by drought. Photo: Darko Vojinovic / AP
"Not easy to explain"
The drought is linked to climate change and Johan Rockström says that southern Europe has become a "hot spot" for extreme weather.
- You can see that the climate is changing faster than expected in central Europe. The UN climate panel warned a few months ago of more drought and more heat waves in Europe, but it is therefore happening faster than we expected.
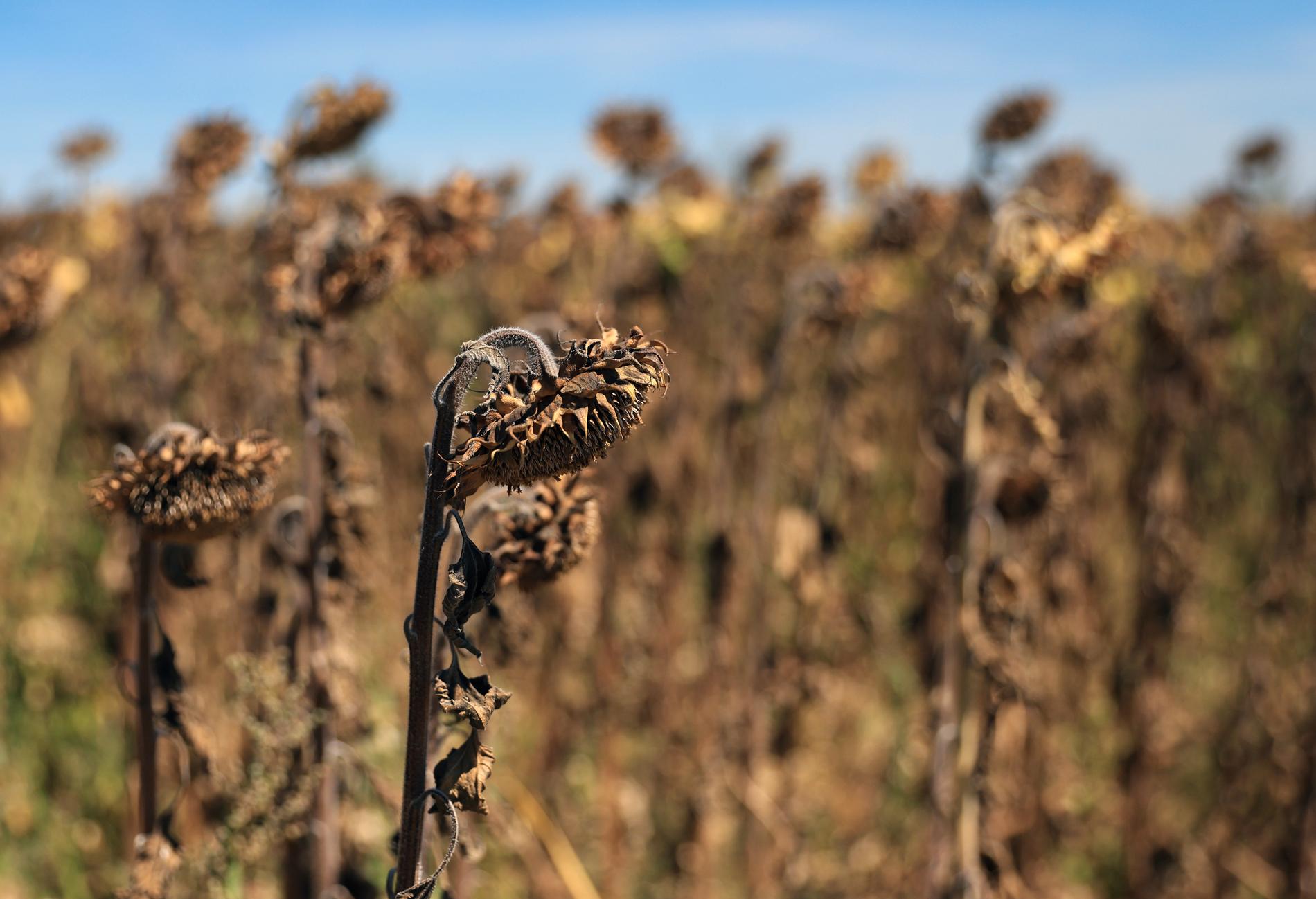

Dried sunflowers south of Paris. Dried sunflowers south of Paris. Photo: Aurelien Morissard / AP
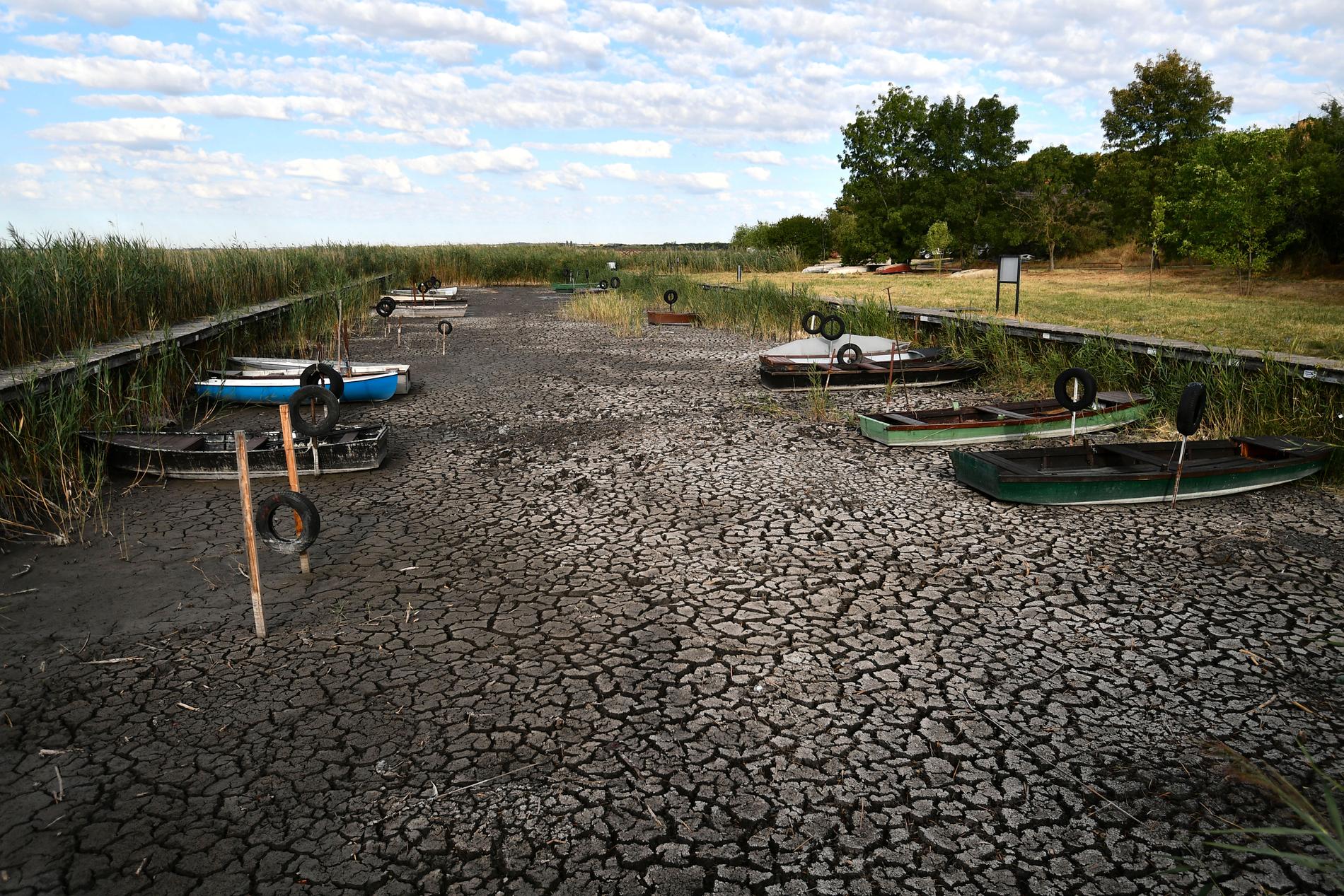

Boats lie on what used to be the seabed in the harbor of Valence, Hungary. Photo: AP
Global warming is seen as one of the reasons for the changes in the climate.
- It is not easy to explain why this is happening so quickly. The global average temperature has increased by 1.2 degrees and now we have another summer with extreme heatwaves.
There are studies that say the only possible explanation is the global temperature rise, he says.
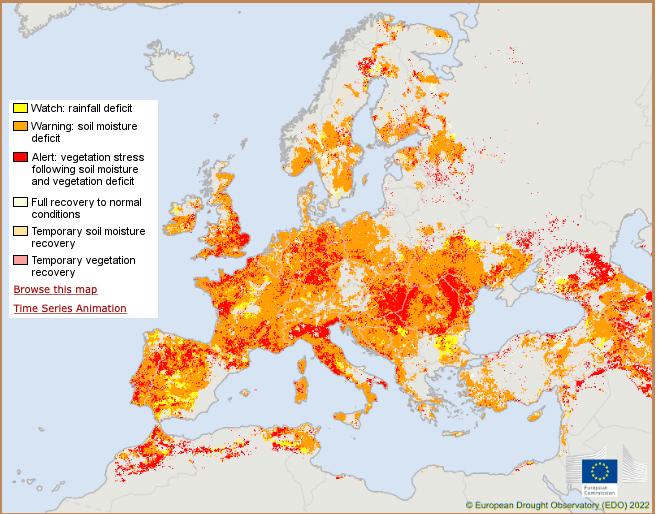
The map from the European Commission's drought observatory.
Drought and water shortages are having serious consequences in Europe. Among other things, the weather risks contributing to water levels reaching such low levels that it becomes difficult to ship important raw materials.
Sweden is also at risk of suffering consequences as a result of the drought, even if the forecasts look better here at home.
- It is very scary. This map is very serious and gloomy. In Sweden, we don't have big problems like other countries in Europe, says Niclas Hjerdt, hydrologist at SMHI.
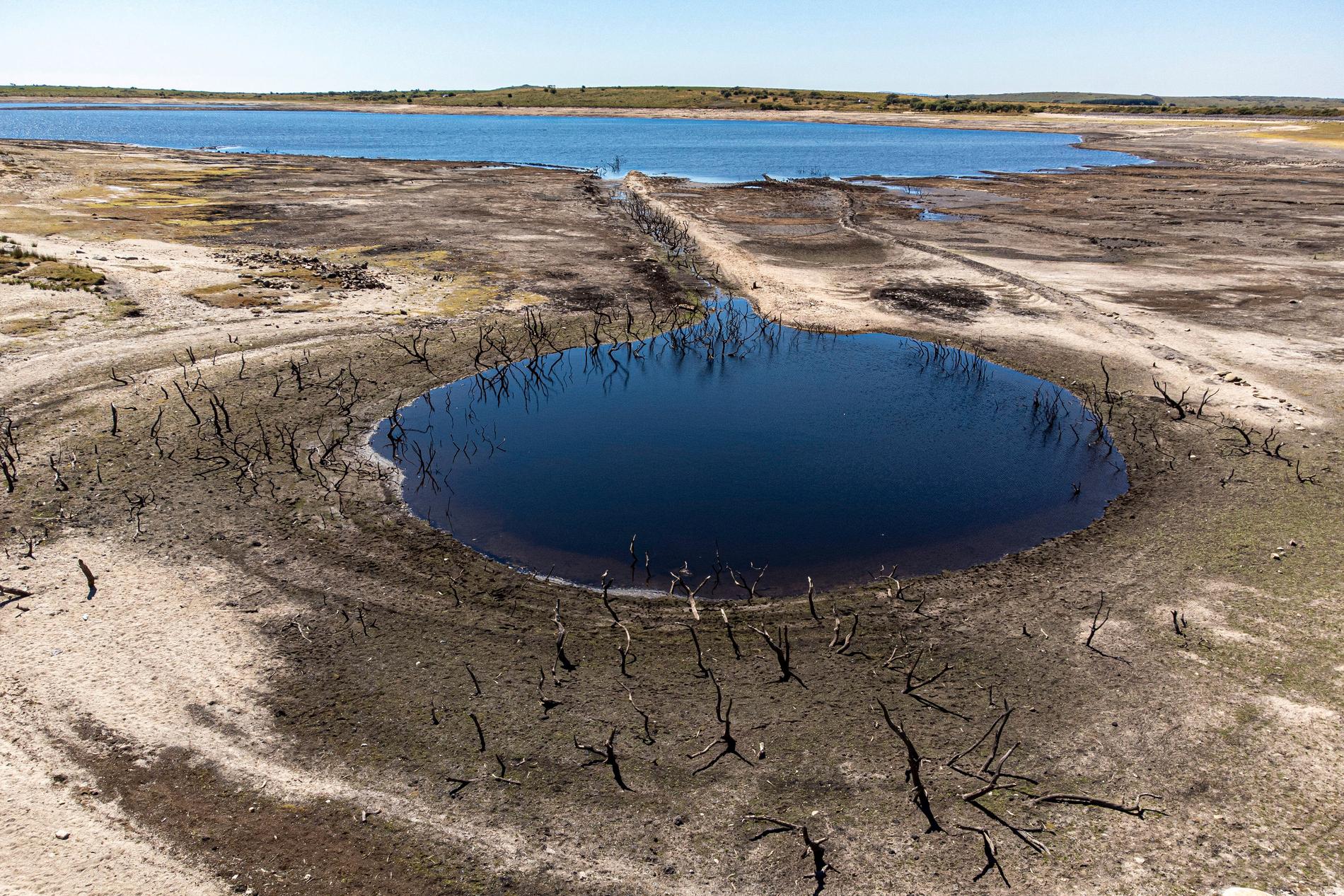

Dead trees and rocks previously hidden by the water have appeared after the drought in Colliford lake in Cornwall. Photo: AP TT NEWS AGENCY
"Worrying trends"
It is mainly the eastern parts of Sweden that are affected.
- We are relatively lucky up here. However, we see that it is very dry in Mälardalen and down towards Blekinge. There they are now talking about the levels being the same as the extreme summer of 2018, says Niclas Hjerdt and continues:
- There are some worrying trends that could mean that we will have more and more problems with water resources in Sweden. It is not a high probability that we will have to manage our water better than before.
He explains that the drought is connected, among other things, to the weather during the winter months when precipitation is needed to fill up water reservoirs. In years with drier weather in the winter, recharge is reduced, which in turn shortens the endurance of water flows during the summer period.
Precipitation that falls during the summer evaporates to a greater extent and does not have as much importance for the level in the water reservoir, says Hjerdt.
- Should we get a few months of abnormally dry weather in the winter, it could have major effects further into next summer.
Inga kommentarer:
Skicka en kommentar